List of Main Exam Tasks
The Main Exam Tasks in will be variations of the tasks from the following list.
Building Trees
In this task, you will build a tree from an intial tree and a sequence of edges. Your task is to iterate through the edge sequence from left to right and expand successively the initial tree. Each edge is a pair
For example, suppose that the initial tree is just a single node (a leaf)
Note that the third edge
Cheap Flights
In this task your goal is to find the cheapest flights from one airport to another. You are given an undirected graph that is represented by a list of nodes (airports) and a list of edges (connections from airport to airport). Each edge contains the two nodes that it connects as well as the cost of traveling along the edge.
Below you can see an exemplary graph with 5 nodes. The cost to travel along an edge is written next to the corresponding edge.
Convex Hull
The convex hull of a set of points is the smallest convex shape that contains the whole set. Fig. 1A shows a set of six points - five of which constitute the \emph{generating points} of their convex hull. In this task you have to find smallest set of generating points of the convex hull of a given set of points.
Figure 1
.
(A): Convex hull of a set of points depicted by the dashed line. The generating points in counter-clockwise order are:
(B): Three of the polar angles
Fermat Primality Test
In this task, for a given natural number
- generate a sequence of pseudorandom natural numbers
such that , - test whether
is prime by checking whether the following equation holds for each generated pseudorandom number
If
Pseudo-random Number Generation
To generate pseudorandom numbers in a given interval, use the Linear Congruential Generator (LCG)
where
The number
Filetree
A filetree can be used to efficiently search/replace in large filesystems. You can think of it as a tree with a variable size of nodes.
You are given a list of files (directories separated by /) like this:
src/tree.hs
src/complex.hs
scripts/ex1/test.ss
scripts/ex1/eval.ss
scripts/emptydir
scripts/ex2/test.ss
tests/test_tree.hsImplement a function which converts the list of files into a tree, and a second function check if a file or directory is already in the tree.
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
In the seminars, we have encountered Deterministic Finite Automata (DFAs). In this task, we will work with a generalized version of the DFA that is called Non-deterministic Finite Automaton (NFA). NFA is the 5-tuple
- set of states
, - a finite set of input symbols
(called alphabet), - a set of transitions
, - a start state
, - a set of final states
.
In other words, NFA is just a directed graph whose vertices are states and transitions are edges labelled by symbols from
An example of an NFA is depicted in the figure below. This NFA accepts e.g. words
Example of NFA where
Text Justification
Given an array of strings words and a width maxWidth, format the text such that each line has exactly maxWidth characters and is fully (left and right) justified.
You should pack your words in a greedy approach; that is, pack as many words as you can in each line. Pad extra spaces ' ' when necessary so that each line has exactly maxWidth characters.
Extra spaces between words should be distributed as evenly as possible. If the number of spaces on a line does not divide evenly between words, the empty slots on the left will be assigned more spaces than the slots on the right.
For the last line of text, it should be left-justified, and no extra space is inserted between words.
Least Common Ancestor
Suppose we have a binary tree
and are descendants of , - if there is a node
having and as descendants, then is descendant of .
To find the least common ancestor of two nodes
- find the path
from the root of to (i.e., a list of nodes starting in and ending in ), - find the path
from to , - consider the common prefix of
and , the last node in the common prefix is the least common ancestor.
Consider, for example, the binary tree depicted below. The least common ancestor of
Similarly, the least common ancestor of
Manhattan Distance
Suppose we have a list of named coordinates:
(define points
'((#\A 1 1)
(#\B 1 6)
(#\C 8 3)
(#\D 3 4)
(#\E 5 5)
(#\F 8 9)))They can be printed on a 2D grid (with dimensions according to the largest x and y coordinates, and (0, 0) on the top left)
.........
.A.......
.........
........C
...D.....
.....E...
.B.......
.........
.........
........FYour task is to fill each . with the lower case letter of the closest coordinate according to the Manhattan distance. We call the resulting grid the nearest-neighbour grid.
aaaaa.ccc
aAaaa.ccc
aaaddeccc
aadddeccC
..dDdeecc
bb.deEeec
bBb.eeee.
bbb.eeeff
bbb.eefff
bbb.ffffFThe grid points which still contain a . represent tied points, i.e. points which have at least two equally close neighbours. The Manhattan distance between two points is defined by
Minesweeper
Implement a program to mark the number of mines directy adjacent (horizontally, vertically and diagonally) to squares on a rectangular Minesweeper field.
Fields with . denote an empty field and * denote mines:
.*.*.
..*..
..*..
.....Your program should output the following
1*3*1
13*31
.2*2.
.111.Minimum Spanning Tree
Given a connected weighted graph
Your task is to implement an algorithm computing the minimum spanning tree, i.e., a function returning for a given connected weighted graph
In chess, a knight can move to any square that is two squares away horizontally and one square away vertically, or two squares vertically and one square horizontally. Therefore, its complete move looks like the letter "L".
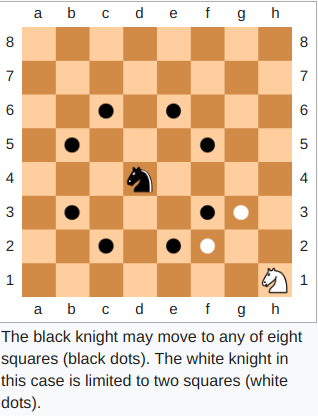
The

Determine the validity of
Photographing Skyscrapers
You are an avid photographer that is obsessed with regular structures and you want to take pictures of cities that are built on regular grids. It turns out that you are also really into roof tops so you want to see as many of them in your pictures as possible. Naturally, you wonder from which side of a given city (North/South/East/West) you should be taking the picture. Luckily a befriended architect gave you maps of the cities you want to photograph. The maps are very simplified and can be represented as lists of lists of integers, so for example in Scheme:
; north
(define city
'((3 0 3 7 3)
(2 5 5 1 2)
(6 5 3 3 2)
(3 3 5 4 9)
(3 5 3 9 0)))
; southEvery number represents the height of a building.
A roof is visible if all other roofs between it and the edge of the grid are smaller than it. Only consider roofs in the same row or column. The first roof at the edge of a grid is always visible.
Pretty Printing of Binary Numbers
The goal of this assignment is to implement a program that reads a positive integer from standard input, converts it into its binary representation, and displays this representation as a text image. Each digit (i.e.,
Implement a program that works as follows:
- Display a message
Enter integer:. - Let the user enter an integer
(you may assume only valid inputs). - Convert
into its binary representation. - Display the binary representation using the above text-images. The particular digits must be separated by a column consisting of the character
'.'.
Below you can see an example run were the user enters the number 12.
Enter integer:
12
...#....#..##...##.
..##...##.#..#.#..#
...#....#.#..#.#..#
...#....#..##...##.Multiplayer Rock, Paper, Scissors
Determine the winner (or remaining players) after several rounds of multiplayer Rock, Paper, Scissors.
Players stand in a circle and all throw at once. If rock, paper, and scissors are all thrown, it is a stalemate, and they rethrow. If only two throws are present, all players with the losing throw are eliminated. The following function decides which throws from a set of set of throws in a single round should be eliminated.
The actions of players are decided in advance; e.g. for two rounds of three-player RPS, the players and actions are represented as:
(define players '("alice" "bob" "charlie"))
(define strategies '((r p) (r r) (s p)))where Alice throws Rock in the first round, then Paper in the second. Charlie never gets to throw his second pick (Paper), as he will be eliminated after one round. Alice is the only remaining player after the two rounds. The result should be '("alice").
You will need to keep track of the players and their actions. In each round, figure out which throws should be eliminated, then filter out the corresponding players and their strategies. Create two helper functions: one that creates a boolean "mask" of all the winners of a single round, and one that performs the filtering.
Sierpinski Carpet
The Sierpiński carpet is a plane fractal first described by Wacław Sierpiński in 1916. Your task is to generate this fractal in a text format represented as a list of strings. Each string represents a single row in the picture. The picture
In other words,
## ### ######### ###########################
# # # ## ## # # ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #
### ######### ###########################
### ### ### ###### ###### ###
# # # # # # # ## # # ## # # #
### ### ### ###### ###### ###
######### ###########################
# ## ## # # ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #
######### ###########################
######### #########
# ## ## # # ## ## #
######### #########
### ### ### ###
# # # # # # # #
### ### ### ###
######### #########
# ## ## # # ## ## #
######### #########
###########################
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #
###########################
### ###### ###### ###
# # # ## # # ## # # #
### ###### ###### ###
###########################
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #
###########################The size of the picture grows exponentially with
Spiral Matrix
A Spiral Matrix is a square
Even though one can define a spiral matrix for each size
where
Square Code
One classic method for composing secret messages is called a square code. First, the input is normalized: the spaces and punctuation are removed from the English text, and the message is downcased. Then, the normalized characters are broken into rows. These rows can be regarded as forming a rectangle. For example, the sentence
If man was meant to stay on the ground, god would have given us roots.is normalized to:
ifmanwasmeanttostayonthegroundgodwouldhavegivenusrootsThe normalized string is 54 characters long, so it is written into a rectangle with 7 rows and 8 columns.
ifmanwas
meanttos
tayonthe
groundgo
dwouldha
vegivenu
srootsNote that the last row is padded with spaces at the end to make it 8 characters long.
The coded message is obtained by reading down the columns going left to right. For example, the message above is coded as:
imtgdvs fearwer mayoogo anouuio ntnnlvt wttddes aohghn sseoauGiven the length
Unit Propagation
The Davis–Putnam–Logemann–Loveland (DPLL) algorithm is the core of SAT solvers nowadays. It takes a propositional formula in CNF (conjunctive normal form) and returns true if, and only if, the formula is satisfiable. A formula in CNF is usually represented as a set of clauses. A clause is represented as a set of literals. A literal is either a propositional variable (e.g.
is represented as
One of the subroutines of the DPLL algorithm is the unit propagation simplifying the input formula. A unit is a clause containing a single literal, e.g.
- if
, then can be removed from , - if
, then can be removed from .
For example, the formula
Your task is to implement the unit propagation for a given formula
while there is a unit clause |{u}| in |φ| do
|φ| <- unit-propagate(u, |φ|);Heap: Balanced Binary Tree
A Heap is a tree that satisfies the heap property: the node's value is greater or equal to the value of any of its children. As a result, the heap's root carries the greatest value in the heap. Hence, heaps are commonly used to implement queue-like data structures. Further, let us consider the heap as a balanced binary tree, where a binary tree is balanced if the heights of the left and right subtree of any node differ by not more than one.
Your task is to implement a function that builds a heap from a given list of elements This function starts with the empty leaf, inserts elements one by one, and fixes the heap property after each insertion.