Lab 4: Higher-order functions and tree recursion
Exercise 1
Write a function (permutations lst) taking a list lst and returning all its permutations. For example
(permutations '(1 2 3)) ; => '((1 2 3) (2 1 3) (2 3 1) (1 3 2) (3 1 2) (3 2 1))Suppose that we have all permutations of a list of length
For instance, ((2 3) (3 2)) are all permutations of the list (2 3). If we want to compute all permutations of (1 2 3), we take each permutation of length 2 and interleave the element 1 into it as follows:
(2 3) => ((1 2 3) (2 1 3) (2 3 1))
(3 2) => ((1 3 2) (3 1 2) (3 2 1))Appending all these lists gives us the desired permutations of (1 2 3).
Write first a function interleave taking an element, a list, and returning all possible ways of inserting the element into the list. Using this function, devise the function permutations using the recursion on the length of lst.
Solution
(define (interleave el lst)
(if (null? lst)
; there is only a single way one can insert el into '()
(list (list el))
; otherwise one possibility is to prepend el to lst
(cons (cons el lst)
; for the rest take all possible insertions of el into (cdr lst)
(map (curry cons (car lst))
; and prepend (car lst) to each of them
(interleave el (cdr lst))))))
(define (permutations lst)
(if (null? lst)
'(())
(apply append
; into each permutation of (cdr lst) interleave (car last)
(map (curry interleave (car lst)) (permutations (cdr lst))))))Note
The permutations function is a great candidate for an application of streams. If you try to run (permutations (range 10)) you will run out of memory with the default DrRacket settings, while you can easily construct a stream of permutations with the (builtin) in-permutations function.
Exercise 2
Binary decision trees represent Boolean functions, i.e., functions from
- Each input variable
induces the th-level in the tree whose nodes are labelled by . - Leaves are elements from
.
Each path from the root to a leaf encodes an evaluation of input variables. If the path in an internal node
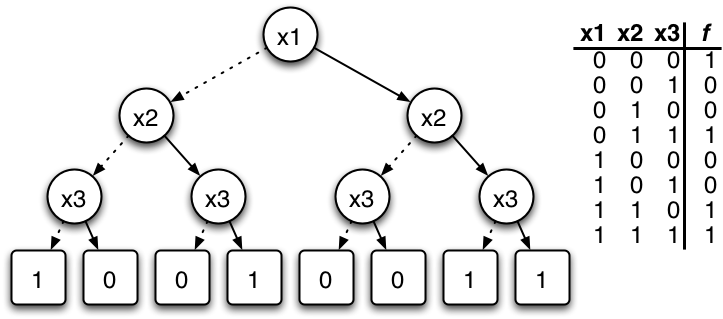
We will represent the inner variable nodes as Racket structures:
(struct node (var left right) #:transparent)For instance, the above tree is represented as follows:
(define bool-tree
(node 'x1
(node 'x2
(node 'x3 1 0)
(node 'x3 0 1))
(node 'x2
(node 'x3 0 0)
(node 'x3 1 1))))Your first task is to implement a function (evaluate tree vals) takes a binary decision tree tree representing a Boolean function vals of values of variables
(evaluate bool-tree '(1 0 1)) => 0
(evaluate bool-tree '(0 1 1)) => 1We devise two versions of evaluate. The first is the recursive function consuming consecutively values of
The second version uses higher-order functions. It converts the list of values of node-left, node-right corresponding to the path defined by vals. Finally, it applies their composition to tree.
Solutions of evaluate
(define (evaluate tree vals)
(match vals
[(list) tree]
[(list 0 vs ...) (evaluate (node-left tree) vs)]
[(list 1 vs ...) (evaluate (node-right tree) vs)]))(define (evaluate tree vals)
; define function 0 -> node-left, 1 -> node-right
; map it over vals, compose the resulting functions and apply to tree
(define (left-right x)
(if (zero? x) node-left node-right))
((apply compose (map left-right (reverse vals))) tree))Exercise 3
Implement a function (satisficing-evaluations tree) which takes a binary decision tree tree representing a Boolean function
(struct assignment (var val) #:transparent)An evaluation is a list of assignments for all variables occurring in the tree. Thus the output of (satisficing-evaluations bool-tree) might look as follows:
(list
(list (assignment 'x1 0) (assignment 'x2 0) (assignment 'x3 0))
(list (assignment 'x1 0) (assignment 'x2 1) (assignment 'x3 1))
(list (assignment 'x1 1) (assignment 'x2 1) (assignment 'x3 0))
(list (assignment 'x1 1) (assignment 'x2 1) (assignment 'x3 1)))The function satisficing-evaluations is a recursive function using an accumulator ev, keeping partial evaluation as we traverse the tree. It recursively finds all satisficing evaluations of the left and right subtree, extends them by
Solution satisficing-evaluations
(define (satisficing-evaluations tree [ev '()])
(match tree
; reverse the evaluation so that the root variable comes first
[1 (list (reverse ev))]
[0 '()]
[(node v l r)
(append (satisficing-evaluations l (cons (assignment v 0) ev))
(satisficing-evaluations r (cons (assignment v 1) ev)))]))Task 1
Write a function (sub-seq lst) taking a list lst and returning a list of all its sublists/subsequences. E.g.
(sub-seq '(1 2 3)) ; => (() (3) (2) (2 3) (1) (1 3) (1 2) (1 2 3))Hint
Code it as a recursive function using the following facts. 1) There is only a single subsequence of the empty list, namely the empty list. 2) Subsequences of
Solution
(define (sub-seq lst)
(if (null? lst)
'(())
(let ([el (car lst)]
[rest-sub-seq (sub-seq (cdr lst))])
(append rest-sub-seq
(map (curry cons el) rest-sub-seq)))))Task 2
Consider a binary tree representing a tournament. Each internal node corresponds to a match. We represent it as the following structure:
(struct mtch (winner left right) #:transparent)Leaves are of the form '<team>. E.g.
(define tour
(mtch 'F
(mtch 'D
(mtch 'A 'A 'B)
(mtch 'D 'C 'D))
(mtch 'F
(mtch 'F 'E 'F)
(mtch 'G 'G 'H))))represents the following tree:
F
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
D F
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
A D F G
/ \ / \ / \ / \
A B C D E F G HWrite a function (beaten-teams tree) taking a binary tournament tree and outputting the list of beaten teams by the winner. E.g., (beaten-teams tour) => (E G D).
Hint
Code it as a recursive function starting in the root defining the tournament winner. Then follow the path labelled by the winner and collects the beaten teams along the path to an accumulator. You can use nested patterns in pattern matching to find out the losers.
Solution
(define (beaten-teams tree [acc '()])
(match tree
[(mtch win win r) (cons r acc)]
[(mtch win l win) (cons l acc)]
[(mtch win (mtch win l r) (mtch los _ _)) (beaten-teams (mtch win l r) (cons los acc))]
[(mtch win (mtch los _ _) (mtch win l r)) (beaten-teams (mtch win l r) (cons los acc))]))